About
About Us
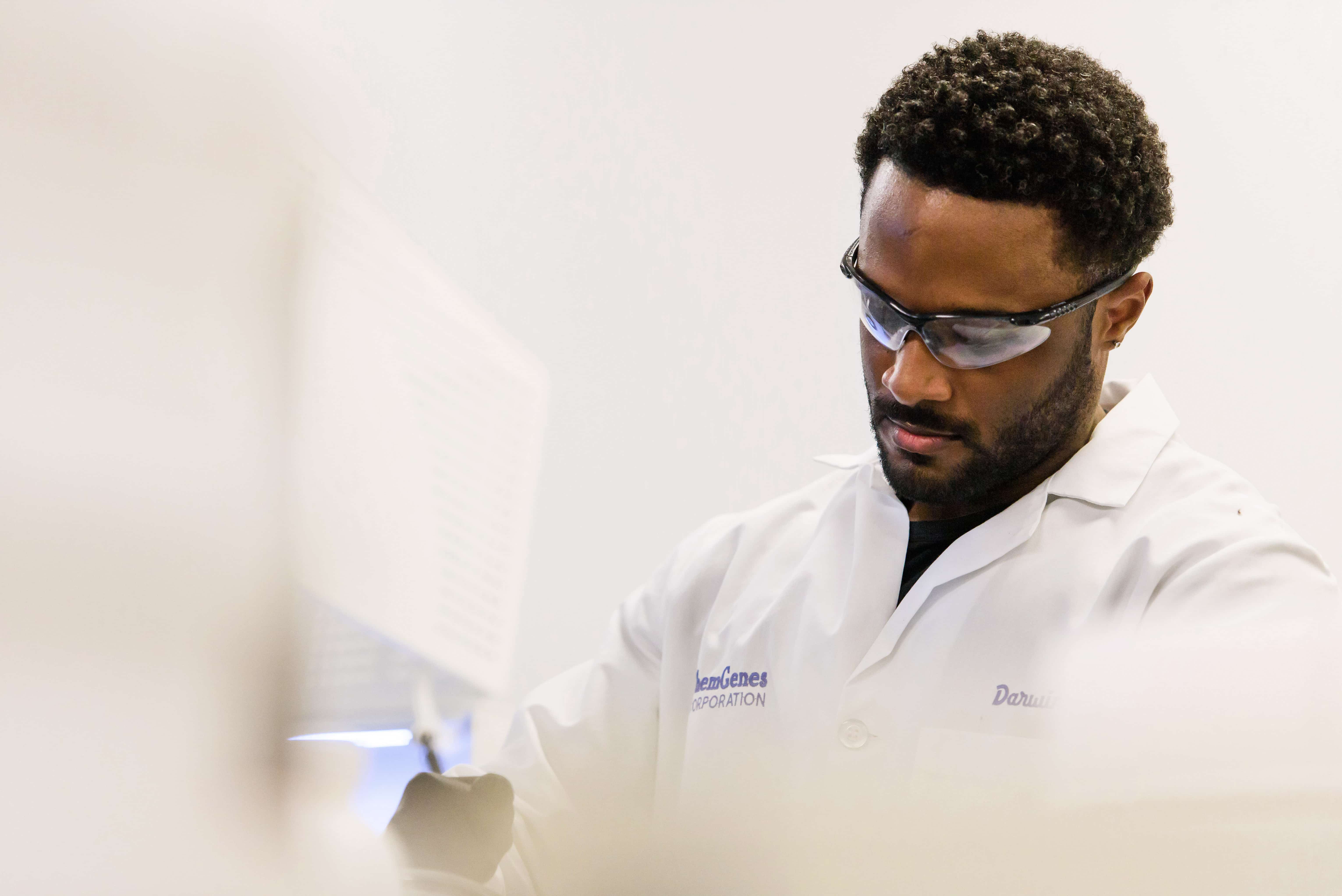

At ChemGenes, we redefine the limits of scientific discovery, development and commercialization by manufacturing the broadest range of modified chemistries available in today’s market.
About ChemGenesYour Account
Orders
Products
- Oligonucleotide Synthesis Reagents
- Mononucleotides & Nucleosides
- Other Reagents
- Specialty Oligoneucleotide Synthesis
- Natural DNA (level 2)
- Modified DNA (level 2)
- Natural RNA
- Modified RNA
- 2' & 3' -O-Methyl RNA
- CombiClick, Combinatorial Click Chemistry
- Chromophores & Ligands
- Ancillary Reagents
- Post Synthesis, Purification, and Accessories
- Morpholinos
- Natural DNA
- Modified DNA
- Natural RNA
- Modified RNA
- 2' & 3' -O-Methyl RNA
- CombiClick, Combinatorial Click Chemistry
- Chromophores & Ligands
- Ancillary Reagents
- Post Synthesis, Purification, and Accessories
- Morpholinos
- 2' & 3' -O-Methyl RNA (level 2)
- Click Chemistry (level 2)
- Chromophores & Ligands
- Ancillary Reagents
- Post Synthesis, Purification, and Accessories
- Morpholinos
- Natural DNA
- Modified DNA
- Natural RNA
- Modified RNA
- Ancillary Reagents (level 3)
- Post Synthesis (level 3)
- Morpholinos
- Natural DNA
- Modified DNA
- 2' & 3' -O-Methyl RNA
- CombiClick, Combinatorial Click Chemistry
- Chromophores & Ligands
- Natural RNA
- Modified RNA
- Ligands (level 3)
- Accessories (level 3)
- Morpholinos
- Natural DNA
- Modified DNA
- 2' & 3' -O-Methyl RNA
- CombiClick, Combinatorial Click Chemistry
- Chromophores & Ligands
- Natural RNA
- Modified RNA
- Modified DNA (level 3)
- Ancillary Reagents (level 3)
- Post Synthesis, Purification, and Accessories
- Morpholinos
- Natural DNA
- 2' & 3' -O-Methyl RNA
- CombiClick, Combinatorial Click Chemistry
- Chromophores & Ligands
- Natural RNA
- Modified RNA
- Chromophores & Ligands (level 3)
- Purification (level 3)
- Morpholinos
- Natural DNA
- Modified DNA
- 2' & 3' -O-Methyl RNA
- CombiClick, Combinatorial Click Chemistry
- Ancillary Reagents
- Natural RNA
- Modified RNA
- Morpholinos (level 4)
- Ancillary Reagents
- Post Synthesis, Purification, and Accessories
- Natural DNA
- Modified DNA
- 2' & 3' -O-Methyl RNA
- CombiClick, Combinatorial Click Chemistry
- Chromophores & Ligands
- Natural RNA
- Modified RNA
- Post Synthesis, Purification, and Accessories (level 4)
- Ancillary Reagents
- Morpholinos
- Natural DNA
- Modified DNA
- 2' & 3' -O-Methyl RNA
- CombiClick, Combinatorial Click Chemistry
- Chromophores & Ligands
- Natural RNA
- Modified RNA
- Lorem ipsum (level 4)
- Ancillary Reagents
- Morpholinos
- Natural DNA
- Modified DNA
- 2' & 3' -O-Methyl RNA
- CombiClick, Combinatorial Click Chemistry
- Chromophores & Ligands
- Natural RNA
- Modified RNA
- Dolor ismet (level 4)
- Ancillary Reagents
- Morpholinos
- Natural DNA
- Modified DNA
- 2' & 3' -O-Methyl RNA
- CombiClick, Combinatorial Click Chemistry
- Chromophores & Ligands
- Natural RNA
- Modified RNA
- Natural RNA (level 4)
- Dolor ismet
- Ancillary Reagents
- Morpholinos
- Natural DNA
- Modified DNA
- 2' & 3' -O-Methyl RNA
- CombiClick, Combinatorial Click Chemistry
- Chromophores & Ligands
- Modified RNA